Catocala consors (J.E. Smith, 1797)
Consort Underwing
NatureServe Global Rank: G4
Virginia State Rank: SH
VA DGIF Tier: IV
Federal Legal Status: None
Virginia Legal Status: None
Description: The Consort Underwing is a large species with a wing span of 60 to 79 mm. Forewings are brownish-gray, often sporting large, dark subreniform spot. Alternating black and yellowish-orange bands on the hind wing are deeply scalloped.
Similar species: Catocala badia has much browner forewings and lacks the deep scalloping pattern on the underwing. The Consort Underwing can be separated from other Underwing species by a combination of the relatively blandly marked front wing and the yellow color of the hind wing.
North American Range: Formerly, much more widespread, today's populations exist mostly in Florida and west to Iowa, Kansas and Texas. There have apparently been no collections from Virginia since the 1960s (Schweitzer et al., 2001) and pre-1960s collections are undocumented at this time.
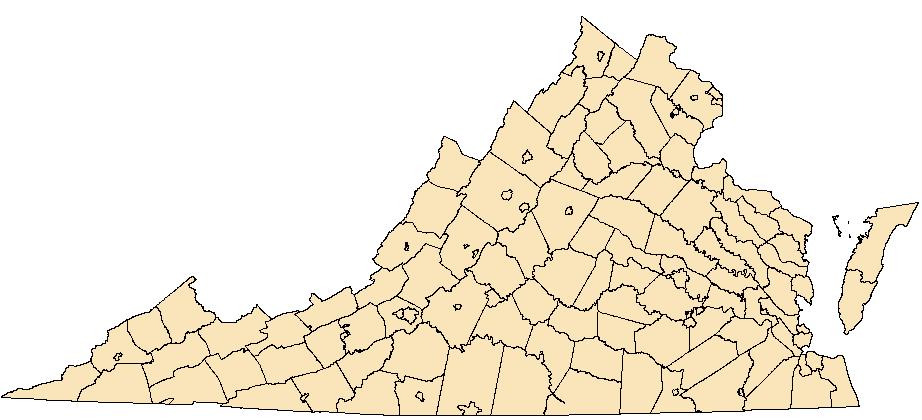
VA Observations by Locality: Mecklenburg

Flight season and broods: June and July.
Habitat and Food Plants: Open, xeric, scrubby, sandy, oak-hickory or oak-pine-hickory woodland and places that have been recently logged or recovering from wildfires. The larva eats spring new growth foliage of small hickories (Carya sp.), mostly on saplings or sprouts less than two meters tall. This species does not require shagbark hickory like several congeneric species do. It sometimes occurs around the edges of savannas and in adjacent, more wooded, habitats.
Behavior and Ecology: Eggs are deposited on tree bark in the fall and hatch the following spring.
Population trend and potential threats: This species has declined in the Eastern United States, but is more common further west. Gypsy Moth (Lymantria dispar) spraying activities are highly detrimental to this species.
Management practices: Frequent prescribed burning could be a negative habitat indicator; however, C. consors could increase after fires that result in abundant hickory sprouts.
References: Covell, C.V., Jr. 1984. Peterson Field Guides: Eastern Moths. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, MA. 496pp.
Moth Photographers Group at the Mississippi Entomological Museum at Mississippi State University. Web application at: http://mothphotographersgroup.msstate.edu/large_map.php?hodges=8772 Accessed: 13Apr2013
Schweitzer, Dale F., Mino, Marc C., Wagner, David L. September 2011. Rare, Declining, and Poorly Known Butterflies and Moths (Lepidoptera) of Forests and Woodlands in the Eastern United States. U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). FHTET-2011-01. Pp. 65, 78, 327-330.
www.silkmoths.bizland.com/catconsors.htm
Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation, Natural Heritage Program, 600 E. Main St., 24th Floor, Richmond, VA 23219
This atlas was compiled
by the VA Natural Heritage Program with funds provided by the VA Dept. of Game and Inland Fisheries through a state wildlife grant
from U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Questions/Comments? Check the contacts page |
Internet Privacy Policy Statement
Last Modified: Friday, 26 February 2021, 03:21:56 PM